Why Your Building Needs a Signal Booster (and How It Actually Works)
Mobile signal boosters are a crucial technology for improving connectivity in areas where network coverage is weak or inconsistent. They work by capturing an existing signal, amplifying it, and redistributing it inside the building.
But what makes them effective, and how do they function on a technical level? This post will break down the core principles of signal boosting, explaining the components, technology, and factors that influence performance.
How Mobile Signal Boosters Work
At their core, mobile signal boosters do three things:
Capture - First, they take an existing mobile signal, which is weak, and pull it in.
Amplify - Then it strengthens the signal by increasing its power while filtering out noise and interference, making it clearer and more reliable.
Rebroadcast - They distribute the improved signal throughout the entire building whether that's small or large.
A mobile signal booster strengthens both uplink (your phone sending data to the network) and downlink (the network sending data to your phone) signals by amplifying the existing connection, reducing interference, and ensuring a more stable and reliable mobile experience.
Uplink: This refers to when your phone communicates with the network, such as making a call, sending a text, or uploading a file. A weak uplink can result in choppy call quality, messages failing to send, or sluggish data speeds.
Downlink: This is when the network sends data back to your phone, including incoming calls, texts, and internet data. Poor downlink signal can cause dropped calls, buffering video, or painfully slow downloads.
Unlike Wi-Fi or network extenders, which rely on broadband connections, signal boosters work with all mobile devices. They don’t create new signal; they improve the one that already exists, ensuring better coverage inside buildings where signals typically struggle to penetrate.
The Key Components of a Mobile Signal Booster
A mobile signal booster system isn’t just a single device - it’s a combination of components working together to enhance connectivity. Let’s take a look at the key parts:
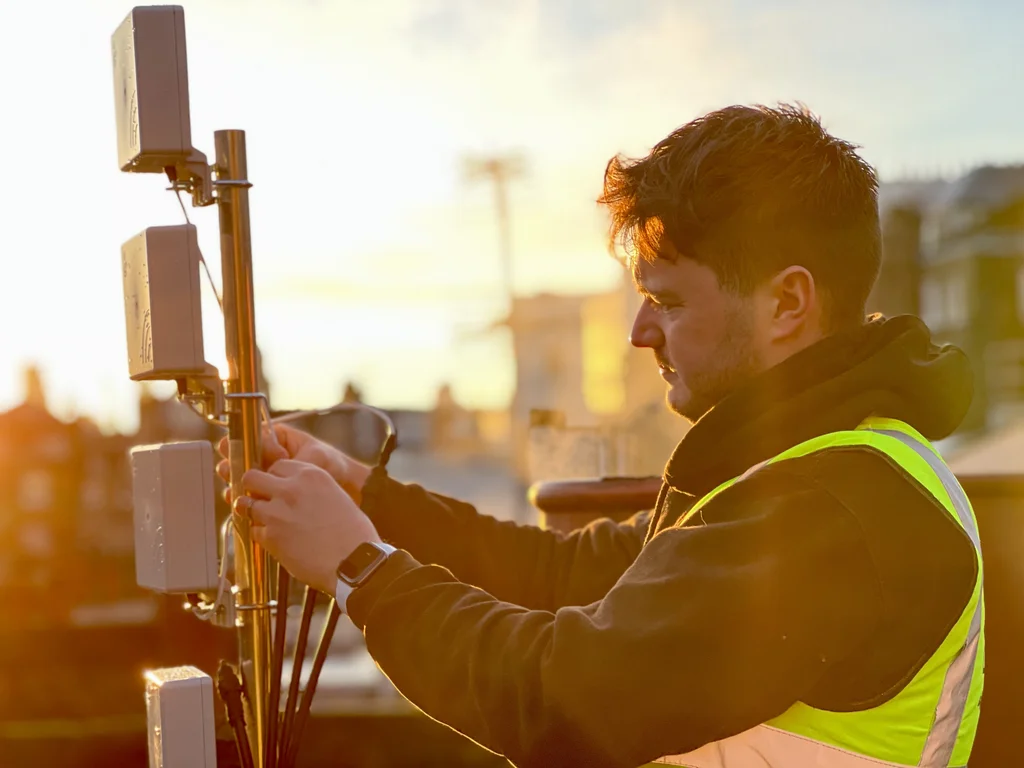
1. External Antenna (Donor Antenna)
The first step is capturing the mobile signal, and that’s the job of the external antenna. Installed on the outside of a building (usually on the roof or an external wall), this antenna picks up the best possible signal from the nearest mobile network tower.
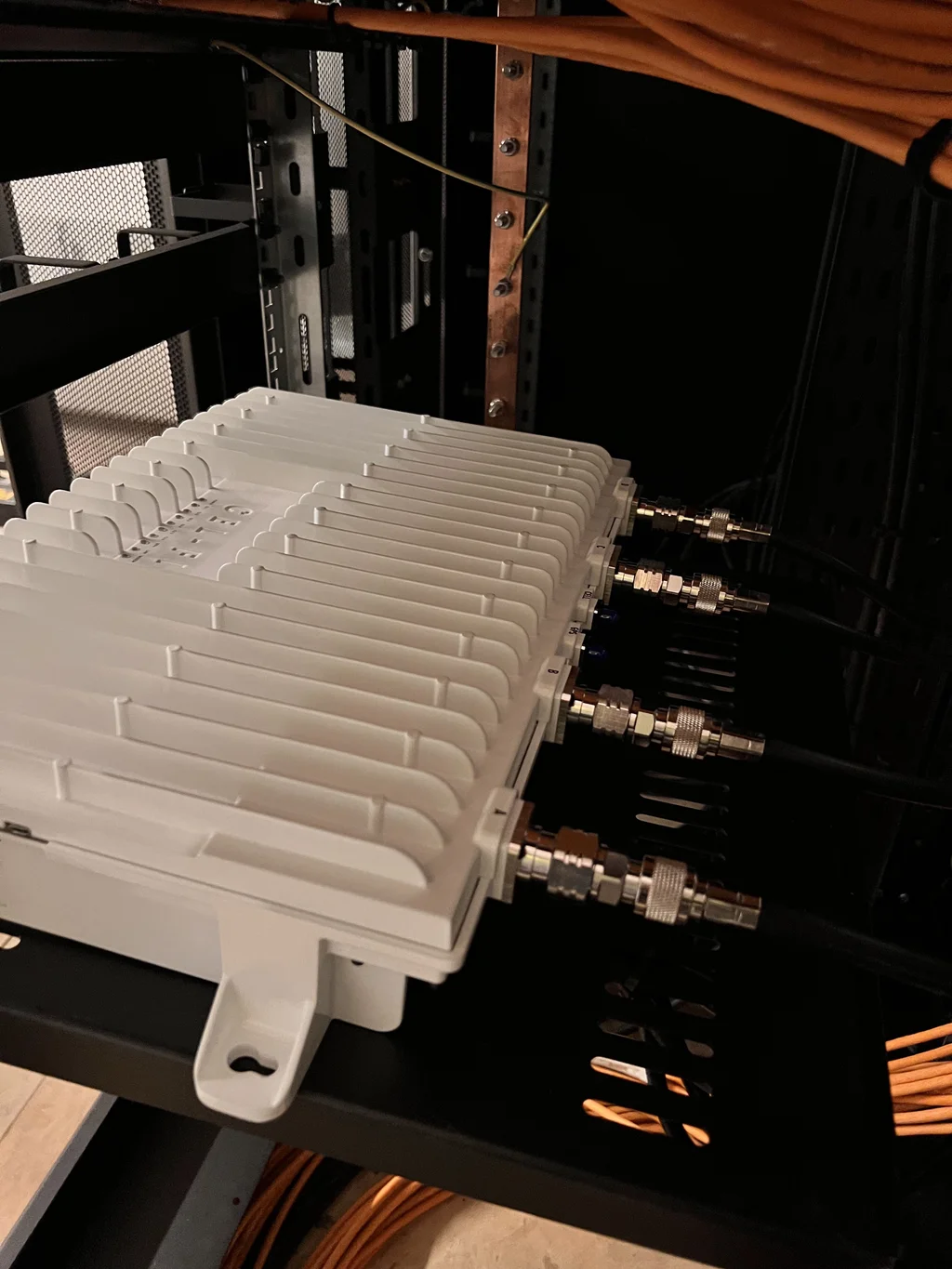
2. Network Unit (Signal Amplifier)
Once the signal is captured, it’s passed to the network unit, which is responsible for boosting it. This device strengthens the weak signal and eliminates noise and interference, ensuring the best possible quality before rebroadcasting it.
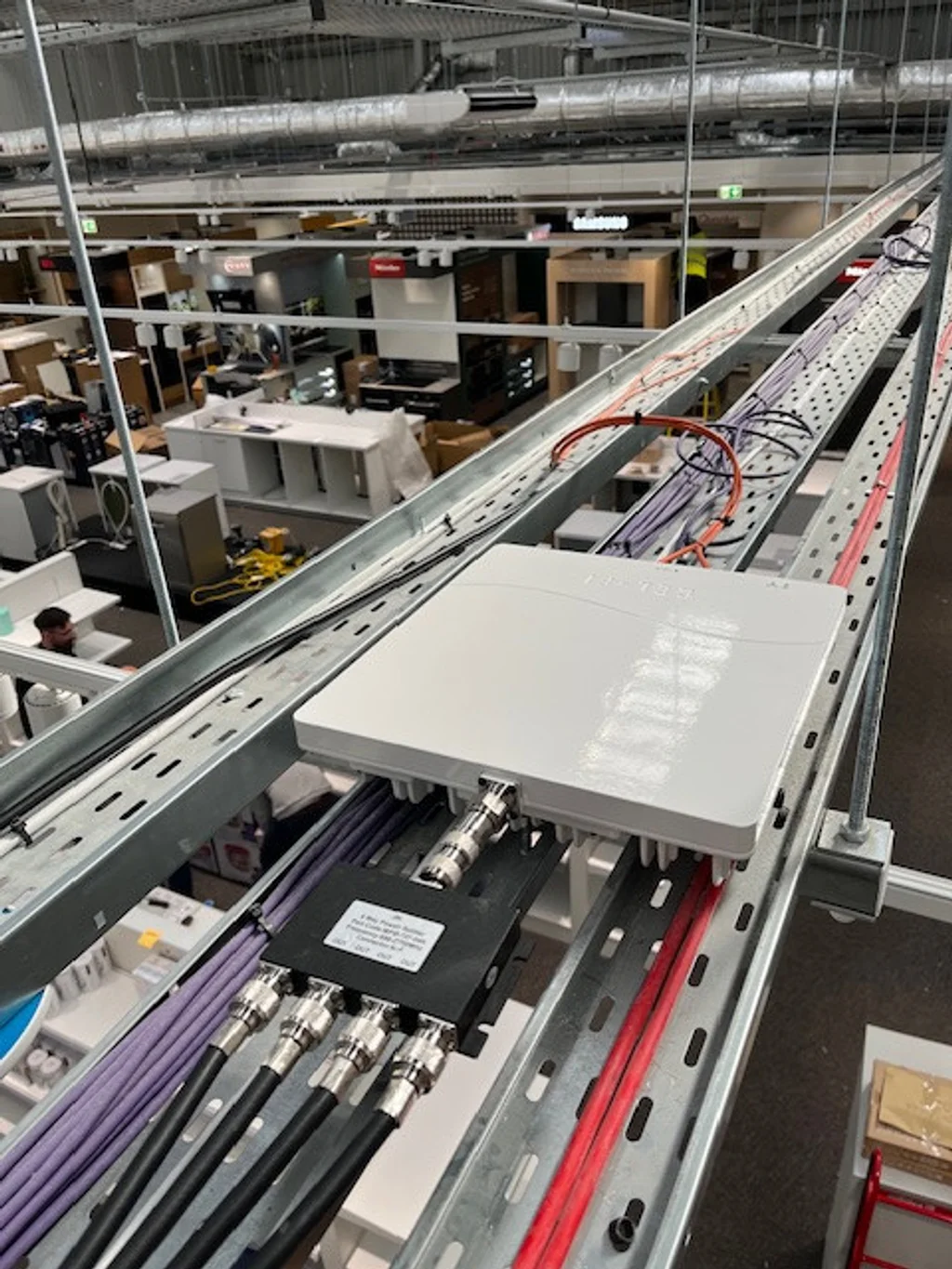
3. Coverage Units
For larger buildings or areas with tricky layouts, a coverage unit may be required to ensure signal is evenly distributed throughout the space. These units work in a series, relaying the amplified signal across different sections of a building to eliminate 'dead zones'.
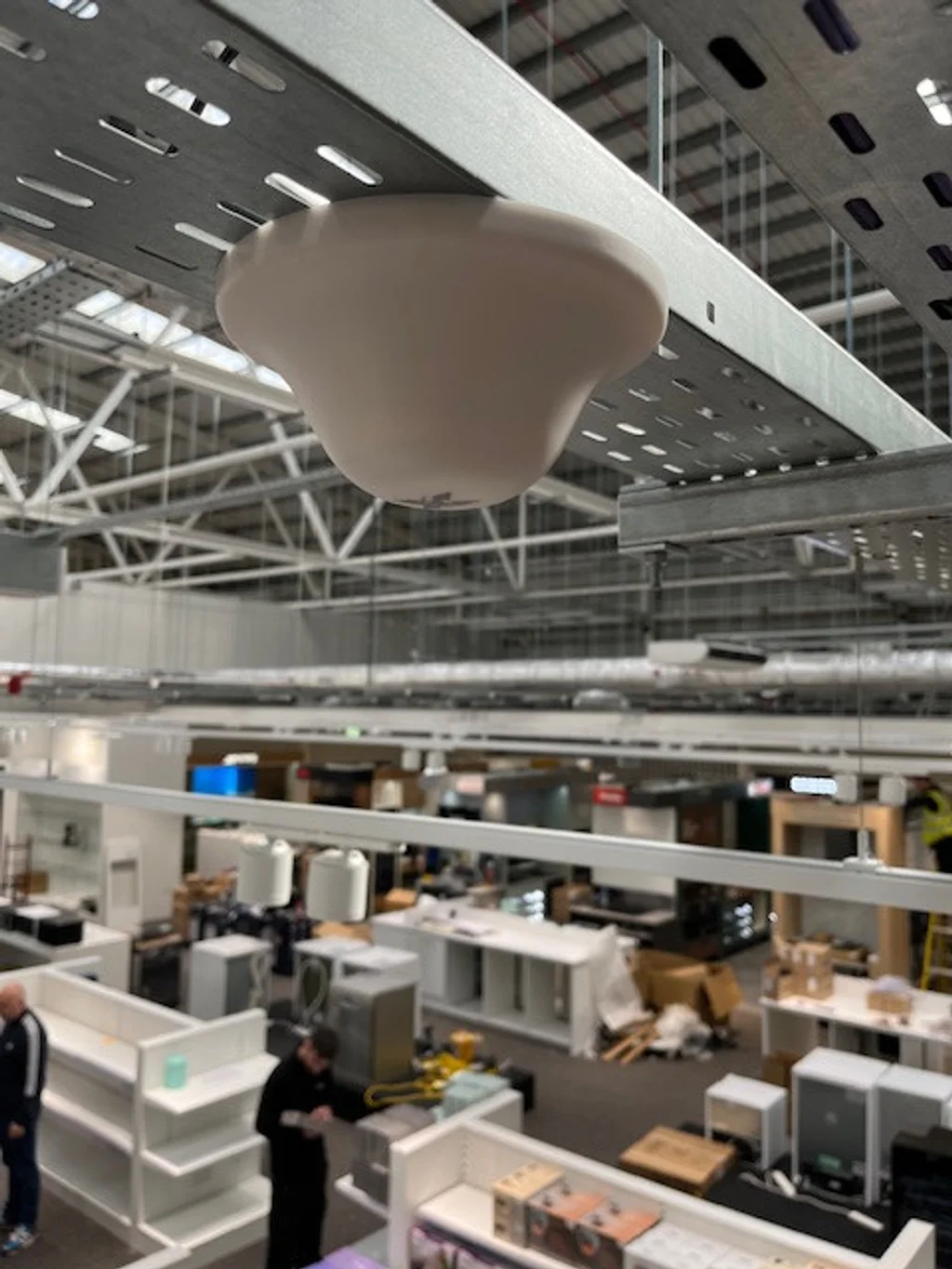
4. Internal Antenna (Service Antenna)
Once the coverage units have extended the signal across different sections of the building, the final step is distributing it to users. That’s where the internal antenna comes in. It rebroadcasts the enhanced signal, allowing mobile devices to connect seamlessly. Internal antennas typically cover a single area, so you might find a few spread out across one floor of a building.
5. Fibre Connectivity for Large-Scale Solutions
In some cases, particularly for large commercial buildings, fibre-connection can be used. Fibre cables can carry the mobile signal over longer distances, helping to distribute it evenly across a large site without losing strength. But fibre isn’t just for big buildings - we've helped Firmdale Hotels link two nearby buildings together, letting them share the same boosted signal!
Factors That Affect Signal Booster Performance
Before installing a mobile signal booster, there are a few common obstacles that might be affecting your connectivity. These challenges listed below are exactly what signal boosters are designed to overcome. Here’s what you might be dealing with now and how a booster can fix it:
Existing Signal Strength - As we already know, if you're struggling with weak signal, a booster will amplify and stabilise it, ensuring strong and reliable coverage.
Building Materials - Concrete, metal, and energy-efficient glass can block mobile signals. A booster cuts through these barriers by catching it from outside and bringing the signal in through the cabling.
Coverage Area - Larger spaces sometimes suffer from patchy coverage. A properly installed booster system, with multiple antennas and coverage units, ensures consistent signal throughout.
Network Compatibility - Signal boosters work across all major networks, so you’ll stay connected no matter which provider you use.
At Signal Solutions, we carefully assess each location to design the perfect solution, eliminating these issues and delivering seamless mobile coverage.
Why Mobile Signal Boosters Are A Reliable Solution
Many people wonder if there are other options beyond signal boosters. While Wi-Fi calling, small cells, mesh networks all exist, they come with limitations.
Wi-Fi Calling - This allows your phone to make calls over a Wi-Fi network instead of using a mobile signal. While useful in some situations, it has drawbacks:
Relies on broadband - If your internet connection is slow or unstable, your call quality will suffer.
Not universally supported - Some mobile networks and phone models may not support Wi-Fi calling.
Limited coverage - If you move out of Wi-Fi range, your call may drop unless your phone seamlessly switches back to the mobile network.
What do you do when WiFi fails and you've got no mobile signal as back up? This could be during a critical work meeting, or when in an emergency with no calls will going through...

Signal Boosters - Enhance signal for all devices and networks, making them the most universal and effective solution. Unlike Wi-Fi calling or small cells, they:
Work with all network - No matter which carrier you use, your signal is improved.
Don’t rely on broadband - They amplify real mobile signals, so even if your internet goes down, your mobile connection remains strong.
Provide consistent coverage - They ensure reliable mobile service throughout your building, regardless of your internet speed.
Safe and network-friendly - Nextivity CEL-FI signal boosters meet Ofcom regulations, ensuring they don’t interfere with mobile networks or other wireless devices, unlike illegal boosters that can cause network disruption.
No security risks - Public Wi-Fi networks can be vulnerable to cyber threats, whereas mobile signal boosters provide a direct, secure connection to your mobile network, reducing risks associated with hacking or data breaches.

We use Nextivity CEL-FI mobile signal boosters to provide a legal, effective and reliable solution to improve connectivity in homes, offices, and commercial buildings. They don’t just increase bars on your phone - they provide strong and clear mobile communication.
Whether you’re dealing with dropped calls, slow data, or frustrating 'dead zones', a properly installed signal booster can make all the difference. Contact us today if you have any questions!



